
The arrangement and identity of transcriptional accesory proteins, also called transcription factors, can be unique for individual genes. Step 4: RNA Processing (pre-mRNA-mRNA) Step 5: Exit. Step 2: Elongation Elongation is the addition of nucleotides to the mRNA strand. It occurs when the enzyme RNA polymerase binds to a. RNA polymerase binds to a promoter (sequence of 3 starter nucleotides). Steps of Transcription Step 1: Initiation Initiation is the beginning of transcription.
TRANSCRIPTION PROCESS 3 STEPS CODE
This process of transcriptional regulation is complex and involves the association of several other proteins in particular arrangements with the transcribed genes. The DNA code is re-written (transcribed) into mRNA with a sequence of bases complementary to DNA. Find a keyword you’re currently ranking within the top 5 positions in Google where there’s a featured snippet and you don’t rank for it. This basic transcriptional complex is likely the same for all genes in all eukaryotic cells, yet it is clear that transcription of selective genes can be on or off, as well as differentially regulated, in distinct cell types to yield different amounts of mRNA. 46 minutes ago &0183 &32 Step 1: Find a featured snippet opportunity. This scaffolding of protein interactions at the TATA box forms the transcriptional complex. These proteins interact with one another, forming a complex to which RNA polymerase II can bind.

However, RNA polymerase II does not bind to the TATA box without the prior association of several other proteins, including transcription factors TFIID, TFIIA and others, with this DNA region. This protein binds to a DNA sequence, which is known as the TATA box because of the linear arrangement of the DNA sequence and its proximity to the start of transcription. RNA polymerase II is a large protein complex composed of multiple subunits. The protein which synthesizes mRNA is known as RNA polymerase II. The transcription process giving rise to mRNA requires the binding of proteins responsible for RNA synthesis to the DNA template immediately 5′ to the start of transcription. This arrangement suggests that the functional structure of the DNA sequences giving rise to RNAs is modular, with an RNA-encoding region as well as functional regions of sequence both 5′ and 3′ to the transcription unit ( Fig. The linear sequence of the nucleotides contains sequences known as genes which are the regions of genomic DNA that can be copied into RNA.
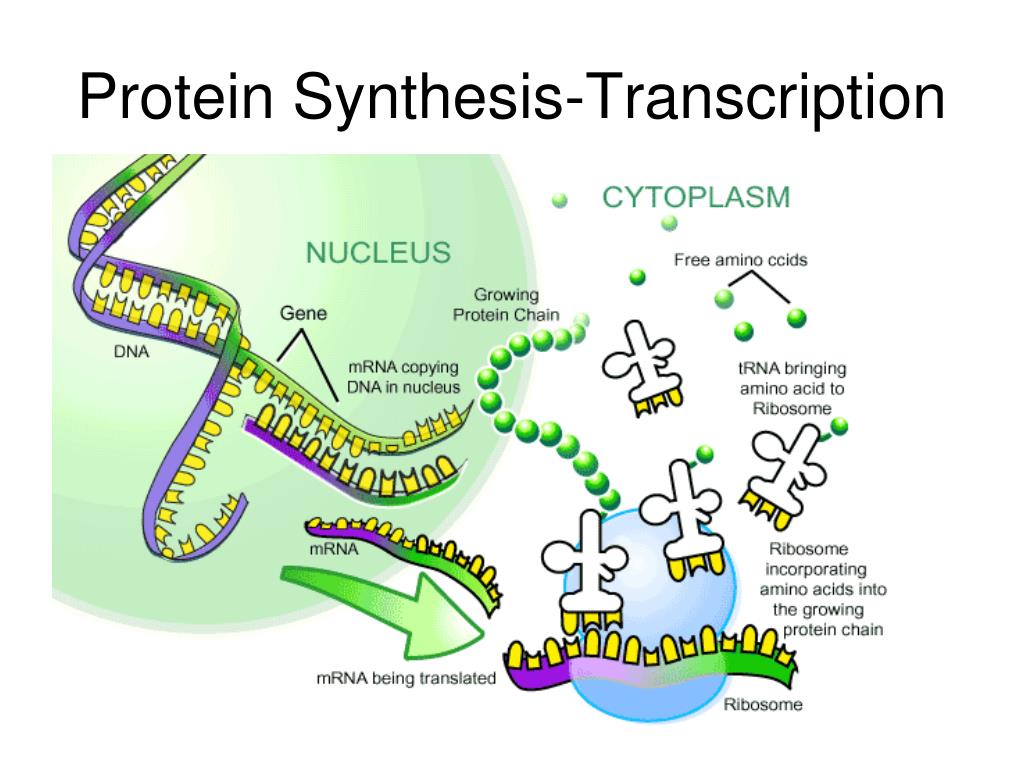
Genomic DNA is double-stranded DNA, oriented in an anti-parallel arrangement such that base pairing of adenosine with thymidine and of guanosine with cytosine will stabilize the structure. DNA is a linear polymer composed of four nucleotides, deoxyadenosine, deoxyguanosine, deoxycytosine and thymidine, which are linked in a linear sequence via phosphate linkages. Learning Outcomes Step 1: Initiation Initiation is the beginning of transcription. Transcription is the process by which RNA is made from genomic DNA. To understand regulation of transcription, it is necessary to categorize the molecules involved.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
